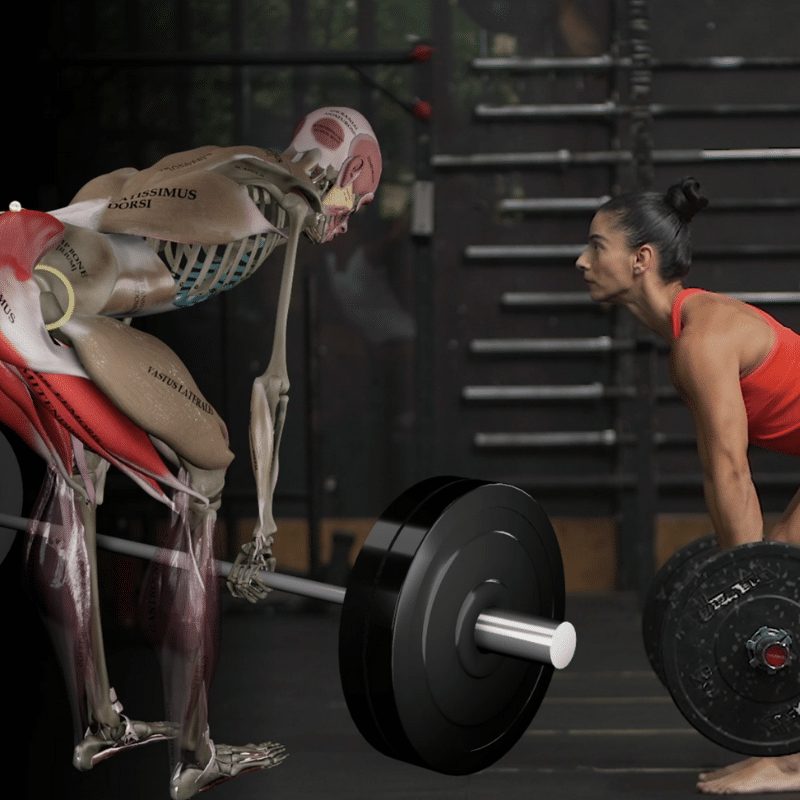Strength training, often perceived as a male-dominated activity, is equally crucial and beneficial for women. Despite the clear advantages, many women shy away from weight training, driven by the myth that lifting weights will make them look “bulky.” In reality, this misconception couldn’t be further from the truth. Strength training is one of the most effective ways for women to build lean muscle, boost metabolism, and enhance physical and mental well-being.
In this Muscle and Motion guide, we’ll highlight the numerous benefits of strength training for women and provide essential beginner’s strength training workouts plans for women to start your journey to a stronger, healthier self.
Common misconceptions
The fear of “bulking up” is widespread among women, but building significant muscle mass requires years of dedicated training and a particular diet. If it were that easy, every man who lifted weights would look like a bodybuilder. It’s important to understand that muscle growth is proportional to the amount of muscle you already have.[1] Since women naturally have less muscle mass than men, even if they build muscle at a similar rate percentage-wise, the overall increase will be much smaller. This means women can lift weights and still achieve a toned, lean physique without getting “bulky.”
Additionally, building muscle mass is essential to look more toned. Toning relates to the ratio of muscle to body fat: having more muscle improves your appearance and creates a more defined shape, even if you have some body fat.
Why strength training is essential?
As mentioned earlier, many women tend to avoid the weightlifting area at the gym, opting instead for cardio machines. Even those who incorporate some resistance training often prefer group classes like yoga, Pilates, or studio workouts. While these activities are great for overall health, they don’t offer the same muscle-building and strength-enhancing benefits as traditional resistance training, especially regarding efficiency and long-term results.
- Building muscle strength: Strength training sculpts your body and enhances functional strength, making everyday activities easier and safer. According to a study published in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, women who engaged in regular strength training increased their muscle strength by 30-50% over several months.[2] This improvement translates to real-life benefits: exercises like squats strengthen your legs and glutes, making tasks like climbing stairs or lifting heavy objects easier, while deadlifts enhance your lower back and core strength, making it safer and more efficient to carry heavy bags or groceries.
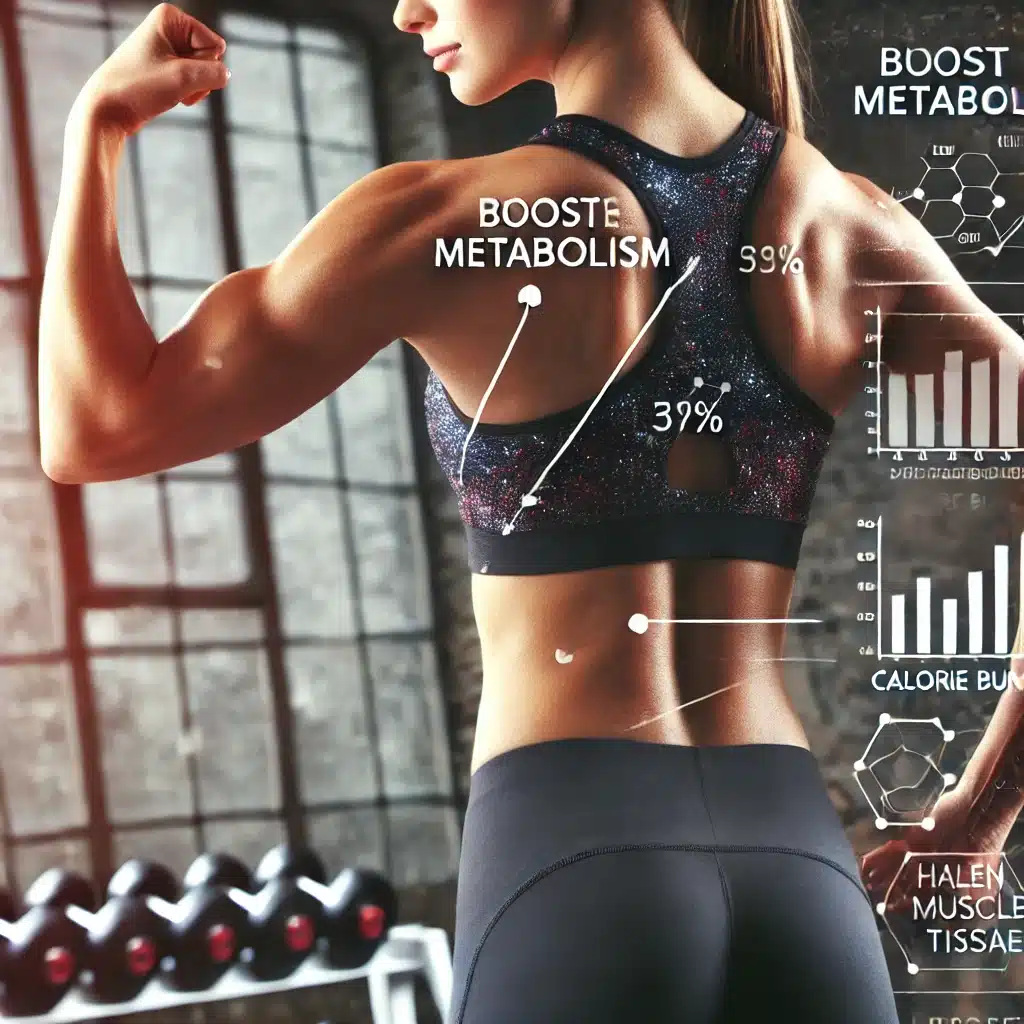
- Boosting metabolism: Lean muscle tissue is highly metabolically active, meaning it burns more calories even when you’re at rest. Your body burns 6-7 calories daily for every pound of muscle gained. While this may seem small, the cumulative effect can significantly aid weight management and weight loss over time. Moreover, having more lean muscle mass has been linked to a reduced risk of developing chronic diseases and lower all-cause mortality. Read the full article Can Lean Muscle Mass Save Your Life for more information.
- Improve bone density: The benefits of strength training extend well beyond aesthetics. It is crucial in maintaining bone health, particularly as women age. According to the National Osteoporosis Foundation, one in two women over the age of 50 will suffer a bone fracture due to osteoporosis. Strength training helps reduce this risk by increasing bone density. For more on how strength training supports bone health, check out the article Enhancing Bone Density Through Exercise.
- Mental health: Strength training is a powerful mood enhancer. A meta-analysis published in JAMA Psychiatry revealed that resistance training is linked to a notable reduction in symptoms of depression.[1] Additionally, women who lift weights often experience a boost in confidence and greater empowerment. For more on how exercise impacts mental health, read the article How Exercise Influences Health and Well-Being.
Despite the benefits, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), only 21% of women in the United States meet the recommended guidelines for aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities.
Beginner’s strength training workout plan for women
It’s time to put aside the myths and embrace strength training as an empowering exercise for the body and mind. So, do women need different workout plans compared to men? The short answer is no. Women can and should train like men, using exercises that engage all major muscle groups. A well-rounded, effective workout plan does not need to be adjusted based on gender; the principles of strength training apply equally.
However, because this guide is tailored for beginners, we’ll focus on full-body workout routines designed to build a solid foundation. These routines ensure that every muscle group is worked evenly, promoting balanced strength and reducing the risk of injury. With these efficient and safe workout plans, you can embark on your strength training journey with confidence.
For additional guidance and tips on getting started, check out our resources: Full-Body Training Programs and First Steps in the Gym.
Full body strength training program
Key details
- Type of workout: Full body, meaning all muscle groups are worked in each session. This approach promotes balanced strength and helps build a strong foundation.
- Training frequency: 2-3 sessions per week. The program is flexible, allowing you to adjust the number of workouts to suit your schedule while still seeing progress.
- Workout duration: 60 minutes. Begin each session with a warm-up using lighter weights and gradually increase to your target weight.
- Rest between sets: Rest for 1-2 minutes between sets, with the exact duration depending on the exercise and individual needs. This time allows for sufficient recovery while maintaining workout intensity.
Workout routine
We’ve chosen some fundamental exercises that are both effective and easy to learn. Click on the name of each exercise to view detailed instructions, including proper techniques and tips for avoiding common mistakes. You can use alternative equipment if you don’t have access to the recommended equipment. Additionally, you can choose a substitute from the “Alternative Exercises” section if you cannot perform a specific exercise.
Workout 1:
- Squats: 3 sets of 8 reps
Focus: Engages quads, glutes, and core - Bench Press: 2 sets of 10-12 reps
Focus: Targets chest, shoulders, and triceps - Bent-Over Row: 2 sets of 12 reps per arm
Focus: Strengthens the back and biceps - Shoulder Press: 2 sets of 10 reps
Focus: Works the shoulders and upper back - Abdominal Crunches: 2 sets of 30-45 seconds
Focus: Improves core stability and strength
Workout 2:
- Deadlifts: 3 sets of 12 reps
Focus: Strengthens the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings - Push-Ups: 2 sets of 10-12 reps
Focus: Engages chest, shoulders, and triceps - Lunges: 2 sets of 12 reps per leg
Focus: Targets quads, glutes, and core - Single-Arm Dumbbell Row: 2 sets of 12 reps per arm
Focus: Works the back and biceps
Workout 3:
- Leg Press (Machine): 2 sets of 12 reps
Focus: Engages the quads, glutes, and hamstrings - Wide-Grip Lat Pulldown: 2 sets of 10-12 reps
Focus: Strengthens the lats and upper back - Close Grip Shoulder Press (Machine): 2 sets of 12 reps
Focus: Isolates the shoulders - Dip Triceps (Machine): 2 sets of 10-12 reps
Focus: Targets the triceps - Russian Twists: 2 sets of 15 reps per side
Focus: Engages the obliques and core
In summary, strength training is a powerful tool for women, providing countless benefits, from building lean muscle and boosting metabolism to enhancing bone health and improving mental well-being.
Following a balanced full-body routine, women can achieve a strong, toned physique without worrying about “bulking up.” Focus on proper form to prevent injuries, progress gradually by increasing weights or reps as you get stronger, and stay consistent to allow your body to adapt and grow. Embrace the strength you build, both physically and mentally, and enjoy the journey to a healthier, more confident you.
Have you ever wondered what makes our anatomical animations so accurate and engaging? Click here to learn about our Quality Commitment and the experts behind our content.
At Muscle and Motion, we believe that knowledge is power, and understanding the ‘why’ behind any exercise is essential for your long-term success.
Let the Strength Training App help you achieve your goals! Sign up for free.
Reference
- Roberts, B. M., Nuckols, G., & Krieger, J. W. (2020). Sex differences in resistance training: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 34(5), 1448–1460.
- Hagstrom, A. D., Marshall, P. W., Halaki, M., & Hackett, D. A. (2020). The effect of resistance training in women on dynamic strength and muscular hypertrophy: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Sports Medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 50(6), 1075–1093.
- Gordon, B. R., McDowell, C. P., Hallgren, M., Meyer, J. D., Lyons, M., & Herring, M. P. (2018). Association of efficacy of resistance exercise training with depressive symptoms: Meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Psychiatry (Chicago, Ill.), 75(6), 566–576.
- Shiroma, E. J., Cook, N. R., Manson, J. E., Moorthy, M. V., Buring, J. E., Rimm, E. B., & Lee, I.-M. (2017). Strength training and the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 49(1), 40–46.