If you ask gym-goers which body part they most want to grow, the answer for many is clear—arms. There’s something undeniably compelling about strong, well-defined arms. They’re more than just a symbol of physical strength; they’re the foundation of an impressive upper body that naturally draws attention.
Whether lifting, pushing or simply going about your day, your arms are always in the spotlight, making their development essential for aesthetics and functionality.
In this Muscle and Motion article, we’re diving deep to create the ultimate guide for arm workouts. We’re not just talking about basic curls and presses—this is your blueprint to building impressive arms with a comprehensive understanding of anatomy and proven training principles. Ready to transform your arms into your most powerful asset? Keep reading, and let’s get started.
Understanding arm anatomy
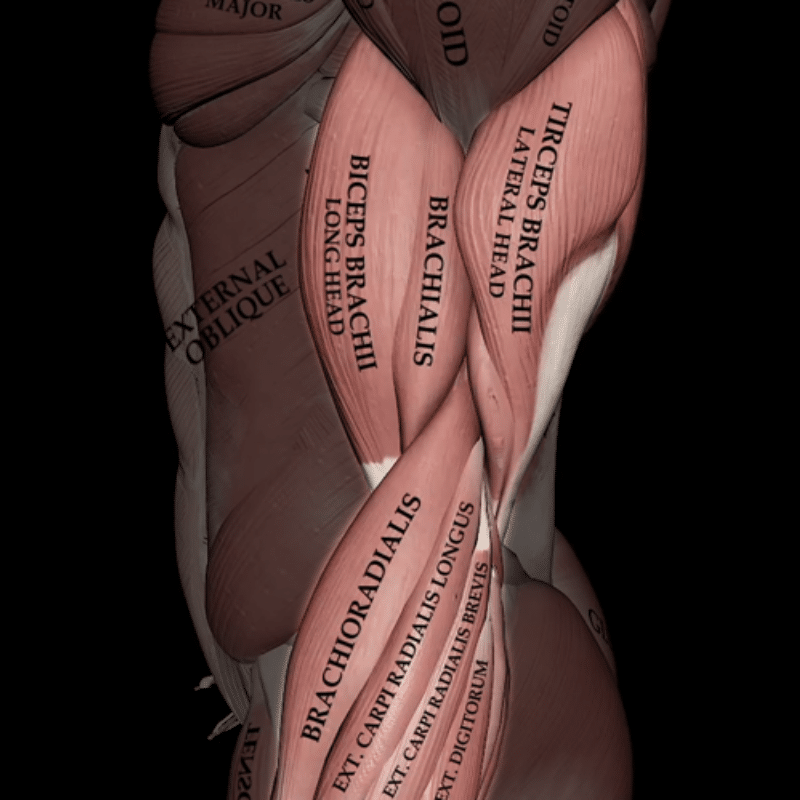
Before diving into the strategies for building bigger arms, it’s crucial to revisit the anatomy of your arm. Understanding the structure of your arm, including the often-overlooked triceps, is essential for a comprehensive approach to arm development. The triceps, located at the back, actually make up about 55% of the upper arm’s muscle mass, compared to the biceps’ 30%.[1] This means that focusing on tricep development is essential if you’re aiming for well-rounded, impressive arms.
- Biceps Brachii: The biceps brachii is found on the front of the upper arm and consists of long and short heads. Its primary functions include elbow flexion, forearm supination, and shoulder flexion. This muscle is crucial for achieving the distinct “bicep peak” many aim for in arms development.
- Triceps Brachii: Located at the back of the upper arm, the triceps brachii comprises three heads: the long head, lateral head, and medial head. Its primary function is elbow extension, which straightens the arm. The triceps dominate the upper arm’s muscle mass and are essential for overall arm strength and size.
- Brachialis: Situated beneath the biceps brachii, the brachialis is primarily responsible for elbow flexion. This powerful muscle plays a significant role in increasing the size and thickness of the upper arm, contributing to a fuller appearance.
- Brachioradialis: The brachioradialis is a prominent muscle in the forearm that assists in elbow flexion. It also plays a role in pronation and supination of the forearm, making it crucial for various arm movements and adding to the overall appearance of the forearm.
Essential tips for maximizing arm growth
To effectively build bigger, stronger arms, it’s crucial to incorporate certain principles into your training regimen. Understanding these principles will help you optimize your workouts for better results.
- Train close to failure: One of the most effective ways to promote muscle hypertrophy is by training close to failure. This approach involves performing each set until you are nearly unable to complete another repetition with good form. This method maximizes the tension in your muscles and promotes greater muscle growth. However, it is essential to balance intensity and recovery, as consistently training to complete failure can lead to overtraining and increased risk of injury. Integrating failure or near-failure sets periodically within your workout routine can help you safely push your limits and enhance muscle development. Want to learn more about this topic? Read our blog: Should You Train to Failure?
- Weekly set recommendations: Research suggests performing at least 10 sets per muscle group weekly to stimulate hypertrophy effectively. Increasing this volume to 20 sets per week for advanced lifters can further enhance muscle growth. However, adjusting your program based on individual recovery capacity is crucial to avoid overtraining.[2]
- Rest between sets: The duration between sets is crucial in maximizing muscle growth. Resting for at least 90 seconds allows sufficient muscle recovery, vital for maintaining workout intensity and promoting hypertrophy. Longer rest periods are especially effective for compound exercises like squats and deadlifts, as they involve multiple muscle groups. Shorter rest intervals can be appropriate for isolation exercises, depending on individual recovery rates and training goals. Proper rest is crucial for maintaining workout volume and ensuring muscle growth. It supports recovery and allows for optimal performance.
- Volume and frequency: Training volume (the total number of sets and reps) and frequency (how often you train) are fundamental to muscle growth. Aim for multiple sets per exercise and target each muscle group 2-3 times per week for optimal arm development. This balanced approach ensures consistent muscle stimulation, promoting growth over time.
- Time under tension: The duration a muscle remains under tension during an exercise is key for muscle hypertrophy. Finding the right balance—neither too long nor too short—helps optimize muscle growth. Performing slow, controlled movements during both the lifting and lowering phases enhances muscle fiber recruitment and promotes greater hypertrophy. To discover the best tempo for maximizing muscle growth, check out our blog: The Role of Time Under Tension In Hypertrophy & Strength.
- Intensity and progressive overload: Finally, progressive overload is key to continuous muscle growth. This principle involves gradually increasing the weight or resistance used in your workouts. By continually challenging your arms with heavier loads or higher reps, you stimulate muscle fibers, leading to increased size and strength.
- Work the muscle in a lengthened position: Recent studies indicate that working muscles in a lengthened position can lead to greater hypertrophy than shorter muscle lengths. For example, starting bicep and tricep exercises in a stretched position has increased muscle growth and strength gains. This approach is particularly effective for exercises like preacher curls and overhead triceps extensions. For more detailed insights, visit our blog: The Role of Stretching and Muscle Length in Hypertrophy.
- Mind-muscle connection: The mind-muscle connection is another critical factor in maximizing arm growth. This technique involves focusing intensely on contracting the target muscles throughout each exercise. By consciously engaging the muscles rather than relying on momentum, you ensure they are fully activated, leading to better muscle development. Various studies related to the upper body, especially the biceps, support this method. For further reading, explore the article on Mind-Muscle Connection.
- Mix up your equipment: Alternating between free weights (dumbbells or barbells) and cable machines can effectively vary the load on your muscles. The maximum resistance shifts between these tools, as cable machines eliminate the gravitational force that impacts free weights. This variation can help target your muscles differently and prevent plateaus in your training progress.
- Balanced nutrition and protein intake: Building muscle requires effective training and proper nutrition. Ensure you’re consuming enough protein, as it’s the building block of muscle tissue. Aim for a balanced diet with proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates to fuel your workouts and support recovery.
- Sleep and recovery: Muscle growth occurs not during the workout but during rest and recovery. To support muscle repair and growth, prioritize getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Proper sleep also helps regulate hormones like cortisol and the growth hormone, which are crucial for muscle development.
Best exercises for building bigger arms
It’s important to include isolation exercises alongside compound movements in your workout routine to build bigger, more muscular arms. While compound exercises like chin-ups and close-grip bench presses target multiple muscle groups and build overall strength, we’ll focus on isolation exercises that specifically target the biceps and triceps. These exercises can be added to your routine to ensure your arms are fully engaged, promoting balanced growth and strength.
Top exercises for elbow flexor muscles development
Incline Dumbbell Curls
Incline dumbbell curls are a must for effectively targeting the long head of the biceps. By performing this exercise on an incline bench, you place the long head in a stretched position, which increases muscle tension throughout the lift. This enhanced tension promotes greater muscle growth. The brachialis and brachioradialis also assist in elbow flexion during this exercise, making it a comprehensive movement for overall arm development.
How to perform:
- Set an incline bench to about 45 degrees.
- Sit on the bench with your back flat against it, holding a dumbbell in each hand.
- Let your arms hang down straight, palms facing forward.
- Curl the dumbbells up while keeping your upper arms stationary, focusing on squeezing your biceps at the top.
- Slowly lower the weights back to the starting position, maintaining control throughout the movement.
Preacher Curls
Preacher curls are particularly effective for isolating the short head of the biceps. Due to the arm position (shoulder flexion), the long head is slightly shortened, shifting the focus to the shorter head of the biceps and brachialis. This exercise is excellent for developing the inner part of the biceps, adding width and fullness to your arms.
How to perform:
- Sit on a preacher bench with your arms resting on the pad.
- Hold a barbell or an EZ curl bar with an underhand grip.
- Slowly curl the weight upward, keeping your upper arms on the pad.
- Squeeze your biceps at the top of the movement before lowering the weight back down with control.
Hammer Curls
Hammer curls, due to their neutral hand position (mid-position), primarily engage the brachioradialis. This exercise not only targets the long head of the biceps but also heavily involves the brachialis, contributing to the overall thickness and strength of the upper arm.
How to perform:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand with a neutral grip (palms facing each other).
- Keep your elbows close to your torso as you curl the weights up.
- Lower the dumbbells back to the starting position with control.
Reverse Curl
In reverse curls, the hand position is pronated (palm facing down) rather than supinated, as in classic bicep curls. This pronated grip shifts the emphasis to the brachialis, making it the dominant muscle during the lift. Reverse curls are particularly effective for building the lower portion of the upper arm and enhancing overall arm size.
How to perform:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell with an overhand (pronated) grip.
- Keep your elbows close to your torso as you curl the weight up.
- Focus on keeping your wrists straight and lowering the bar slowly after each rep.
Top exercises for triceps development
When training the triceps, it’s essential to work the muscle in different positions and with varying levels of stretch to engage all three heads and promote optimal growth fully.
Overhead Triceps Extensions
This exercisefully stretches the triceps by extending the shoulder into full flexion, effectively engaging all three triceps brachii heads. Training the triceps in this elongated position has significantly enhanced hypertrophy. Overhead triceps extensions are particularly effective for adding substantial mass and shape to the back of the arm, making them a vital component of any comprehensive triceps workout.
How to perform:
- Stand facing away from the machine, holding the rope overhead with arms fully extended.
- With elbows pointing forward, lower the rope behind your head by bending your elbows.
- Extend your arms back to the starting position, focusing on squeezing the triceps.
Skull Crushers (Lying Triceps Extensions)
Skull crushers work the triceps in a partially stretched position, with the shoulder at a 90-degree angle, which partially lengthens the muscle. This exercise isolates the triceps by focusing on elbow extension, particularly targeting the long head, promoting overall tricep thickness and strength.
How to perform:
- Lie on a bench, holding a barbell with a close grip and with arms extended straight up.
- Lower the barbell towards your forehead by bending your elbows, keeping your upper arms stationary.
- Press the barbell back up to the starting position, focusing on extending the elbows.
Tricep Push-downs
Tricep pushdowns effectively target the triceps while maintaining a neutral position throughout the movement. A cable machine ensures constant tension on the muscle from start to finish, maximizing muscle engagement and promoting optimal growth.
How to perform:
- Stand facing a cable machine, holding the rope or bar attachment with an overhand grip.
- Keep your elbows close to your sides as you push the attachment down.
- Fully extend your arms at the bottom before returning to the starting position.
Tricep Dips
Tricep dips are a bodyweight exercise that places the long head of the triceps in a shortened position at the shoulder, introducing a unique stress to the muscle. This exercise effectively targets all three heads of the triceps and can be intensified by adding weight, making it a versatile option for tricep development and overall arm strength.
How to perform:
- Position yourself on parallel bars or a sturdy bench.
- Lower your body by bending your elbows until your upper arms parallel the ground.
- Push yourself back up to the starting position, keeping your body upright to focus on the triceps.
In summary, achieving strong, impressive arms requires more than just a few basic moves. It’s about integrating a strategic mix of exercises specifically targeting the biceps and triceps while benefiting from compound movements. By following the principles of progressive overload and focusing on muscle engagement, you can drive significant growth and strength.
But this is just the beginning—countless other exercises and tips are available to help you refine your routine. Our Strength Training App offers a wide array of targeted exercises and personalized workout plans designed to help you reach your goals. Sign up for free today and start your journey toward stronger, more defined arms!
Have you ever wondered what makes our anatomical animations so accurate and engaging? Click here to learn about our Quality Commitment and the experts behind our content.
At Muscle and Motion, we believe that knowledge is power, and understanding the ‘why’ behind any exercise is essential for your long-term success.
Let the Strength Training App help you achieve your goals! Sign up for free.
Reference:
- Holzbaur, K. R. S., Murray, W. M., Gold, G. E., & Delp, S. L. (2007). Upper limb muscle volumes in adult subjects. Journal of Biomechanics, 40(4), 742–749.
- Schoenfeld, B. J., Ratamess, N. A., Peterson, M. D., Contreras, B., Sonmez, G. T., & Alvar, B. A. (2014). Effects of different volume-equated resistance training loading strategies on muscular adaptations in well-trained men. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 28(10), 2909–2918.